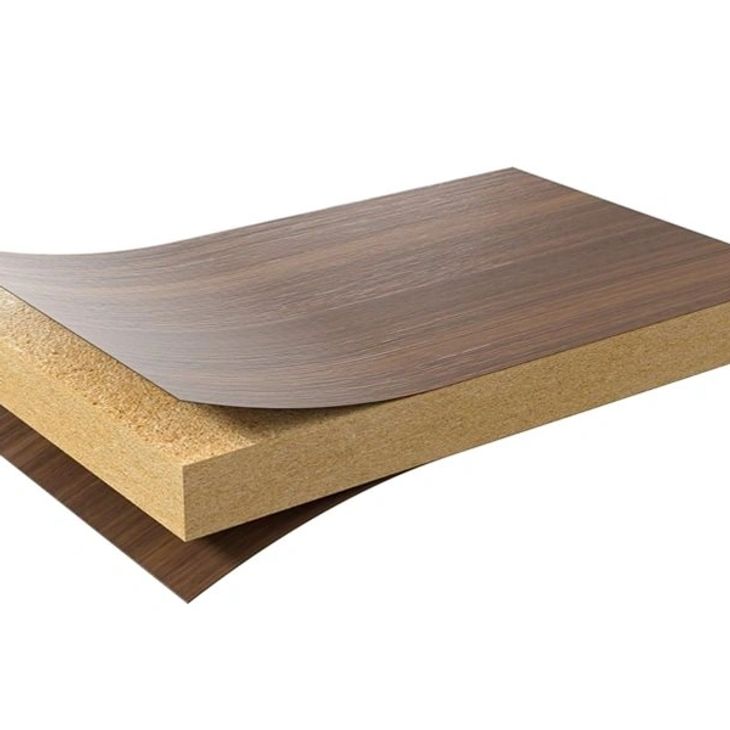
Fiberboards are engineered wood products made from compressed wood fibers and adhesive, offering a wide range of applications in construction, furniture making, and interior design.
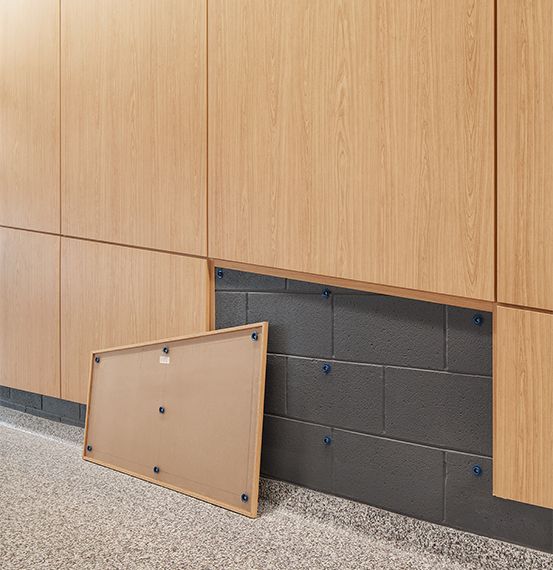
These versatile engineered wood products are made from compressed wood fibers combined with adhesive resins. Due to their uniform density and smooth surface, they provide an ideal substrate for various applications, making them a popular choice in construction, furniture making, and interior design. Available in different densities—such as medium-density fiberboard (MDF) and high-density fiberboard (HDF)—they are valued for their strength, stability, and ease of use. They can be easily cut, shaped, and finished, making them suitable for creating cabinetry, shelving, wall paneling, and flooring. Additionally, they are often used in acoustical treatments, as they can dampen sound effectively. Their adaptability and affordability make them an attractive material for both professional and DIY projects.
Crafted from compressed wood fibers and adhesive, these products offer a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to solid wood. Their production often involves using wood byproducts, such as sawdust and recycled wood fibers, which reduces waste and promotes sustainable resource use. Their flexibility allows manufacturers to create products with various thicknesses and densities, tailored to specific applications. For instance, MDF is popular in cabinetry and furniture due to its smooth surface, which readily accepts paints, veneers, and laminates. HDF, on the other hand, is prized for its durability and is commonly used in flooring and industrial applications where higher strength is needed.
They also offer impressive dimensional stability, as they are less prone to warping or shrinking compared to natural wood. This makes them ideal for interior environments, particularly in regions with fluctuating humidity levels. In addition to structural applications, they are widely used in decorative projects. They can be easily molded, routed, or embossed, providing designers with the flexibility to create intricate patterns and designs.
Beyond aesthetics and functionality, these products contribute to improved indoor air quality. Many modern versions are manufactured with low or no added formaldehyde adhesives, making them a healthier choice for residential and commercial spaces. Their sound-dampening properties also make them valuable in spaces requiring noise control, such as offices, theaters, and recording studios. Overall, they combine affordability, versatility, and sustainability, making them indispensable in both traditional and modern construction and design industries.





Fiberboards offer a wide variety of sizes to meet the requirements of any project. The sizes offered are:
Size of FIberboards :
Thicknesses:
Thicknesses can vary from 1.5mm to 30mm
Emissions:
E0.5, E1, E2









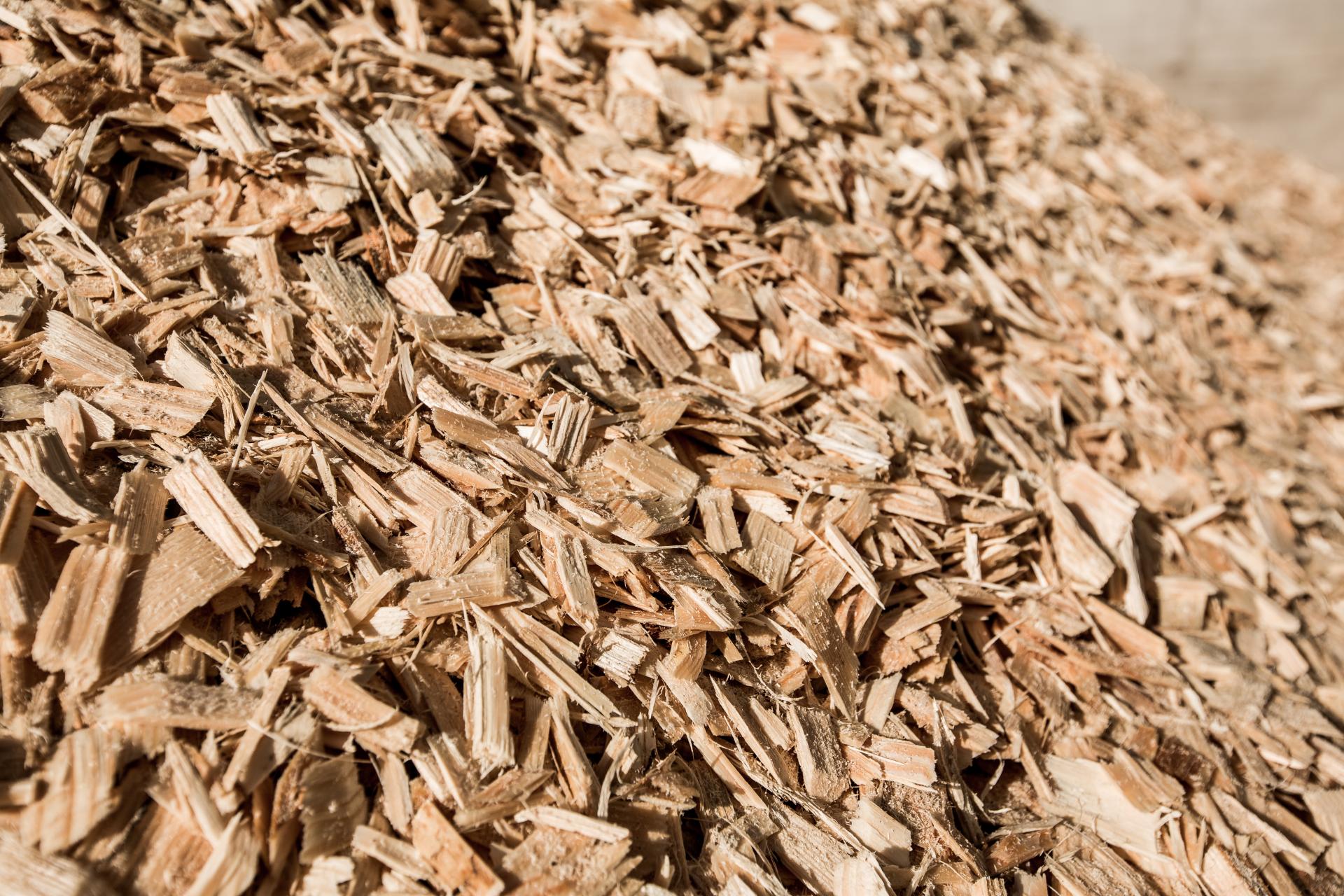
 Wood Chipping
Wood ChippingFresh or recycled wood material is cut and sorted into small pieces of similar size.


 Chips Cleaning
Chips CleaningChips are washed to remove things such as dirt and sand. Metal scraps such as nails can be removed with a magnet placed over a conveyor belt on which the chips move forward.


 Steaming
SteamingIn the case of, for example, MDF (medium density fiberboard) and not particle board, chips are then steamed to soften them for defibration.


 Chemicals Application
Chemicals Application Small amount of paraffin wax is added to the steamed chips and they are transformed into fluffy fibers in a defibrator and soon afterwards sprayed with adhesives such as urea-formaldehyde (UF) or Phenol formaldehyde resin (PF). Wax prevents fibers from clumping together during storage. Chips in the case of particle board are also sprayed with a suitable adhesive before the next steps.

 Pressing
PressingFibers or chips are arranged into a uniform “mat” on a conveyor belt. This mat is pre-compressed and then hot-pressed. Hot-pressing activates the adhesive and glues the fibers or chips together.


 Finishing
FinishingBoard is then cooled, trimmed, sanded and maybe veneered or laminated.







