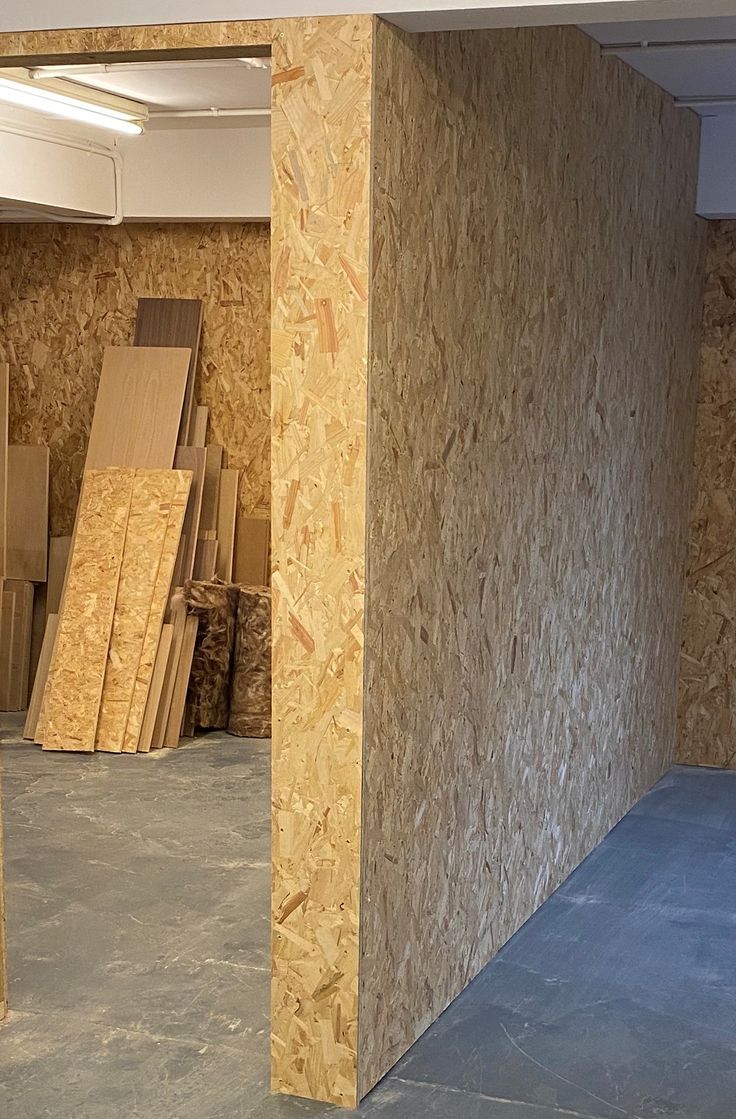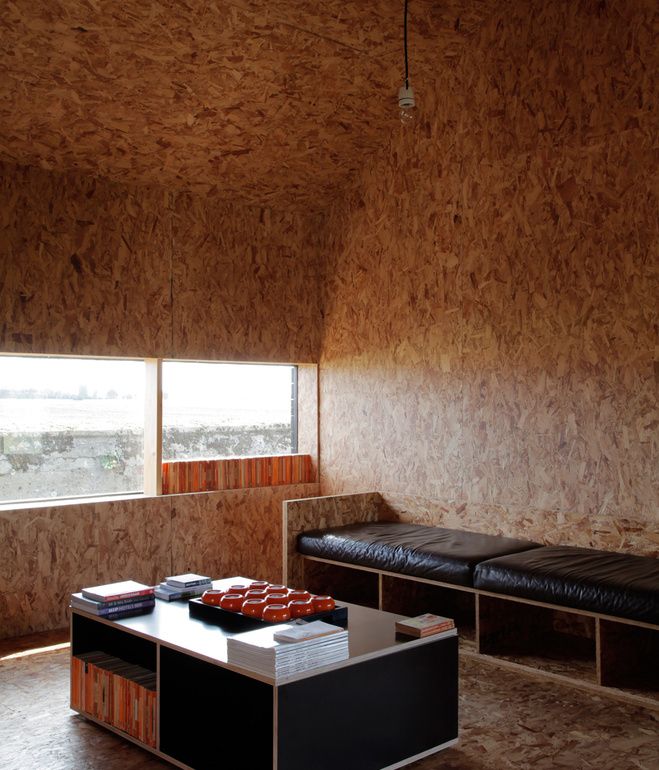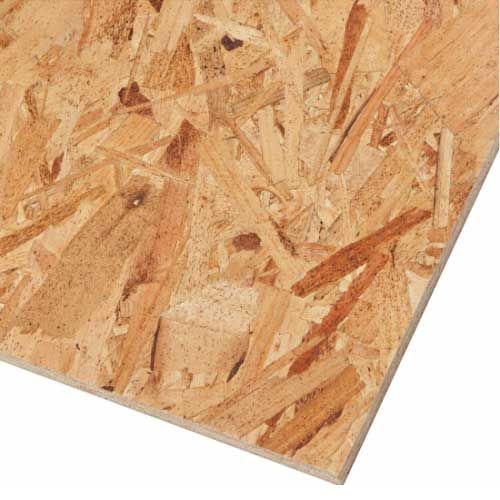
Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood similar to particle board, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood flakes in specific orientations. Osb boards are considered the most popular and most commonly used in construction. These boards are considered as a workhorse of the construction world, offering a strong, affordable, and versatile alternative to plywood. The cross-oriented strands enhance its structural integrity, making it resistant to bending and warping.
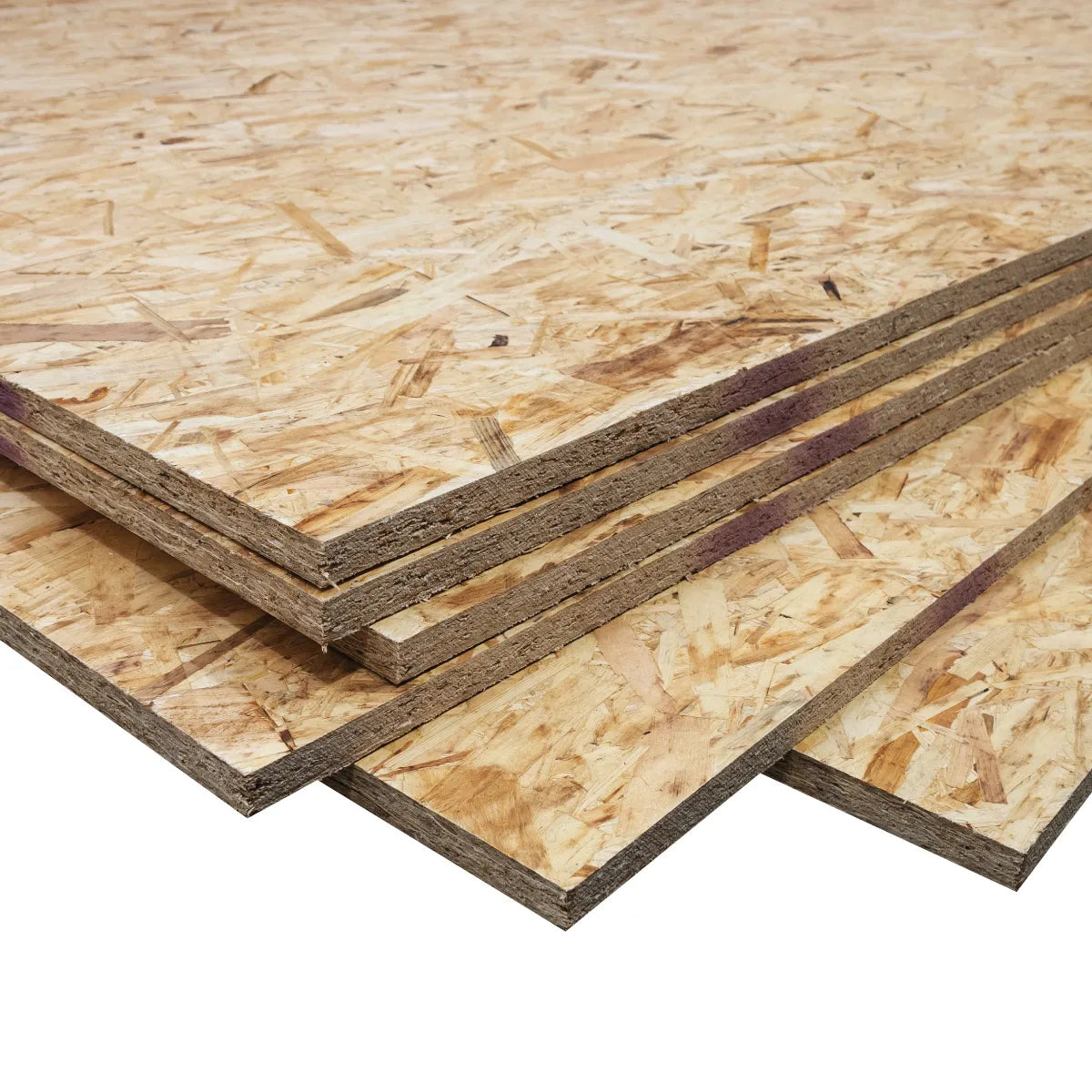
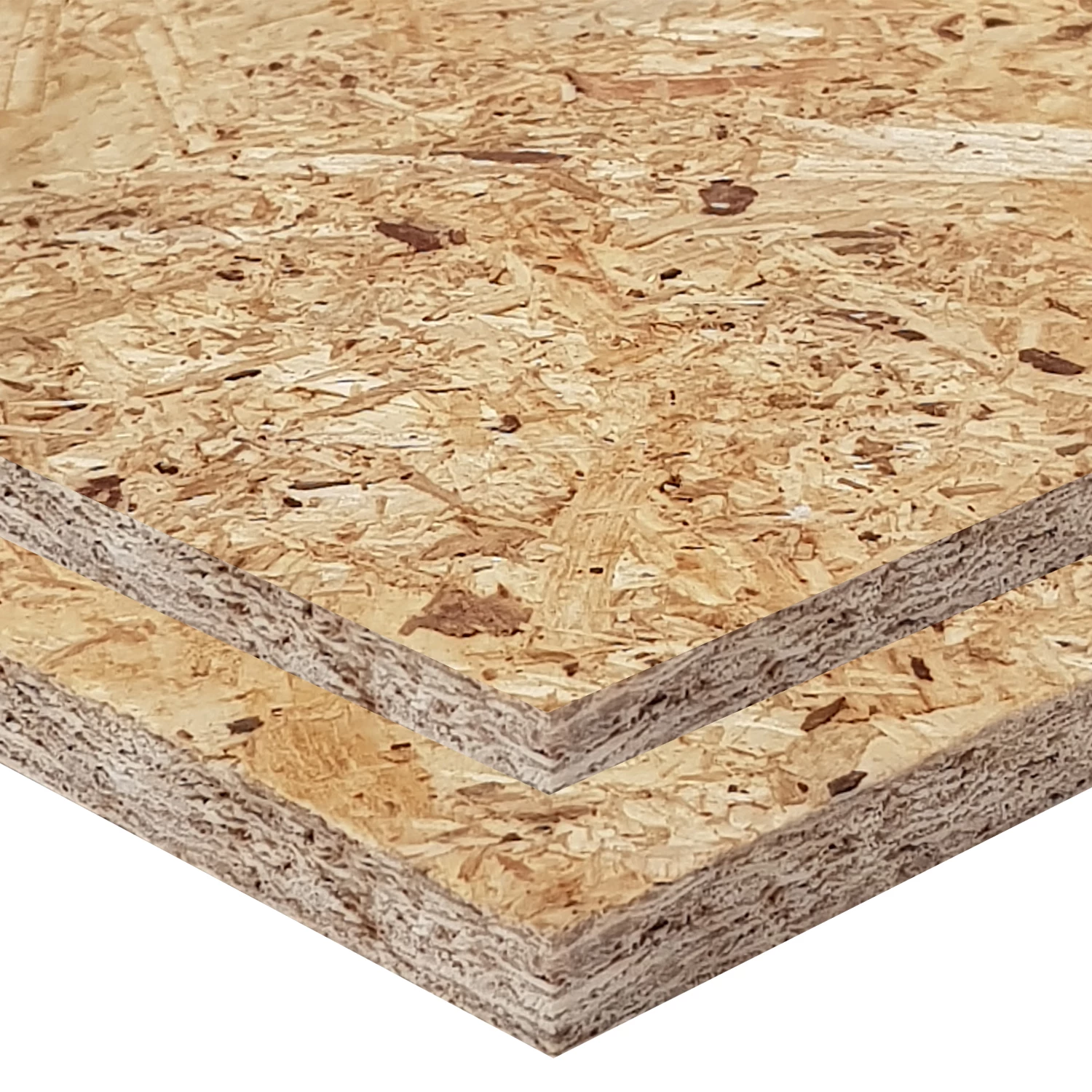





Sizes:
Thicknesses:
Grades:

The manufacturing process of OSB boards involves several key steps:

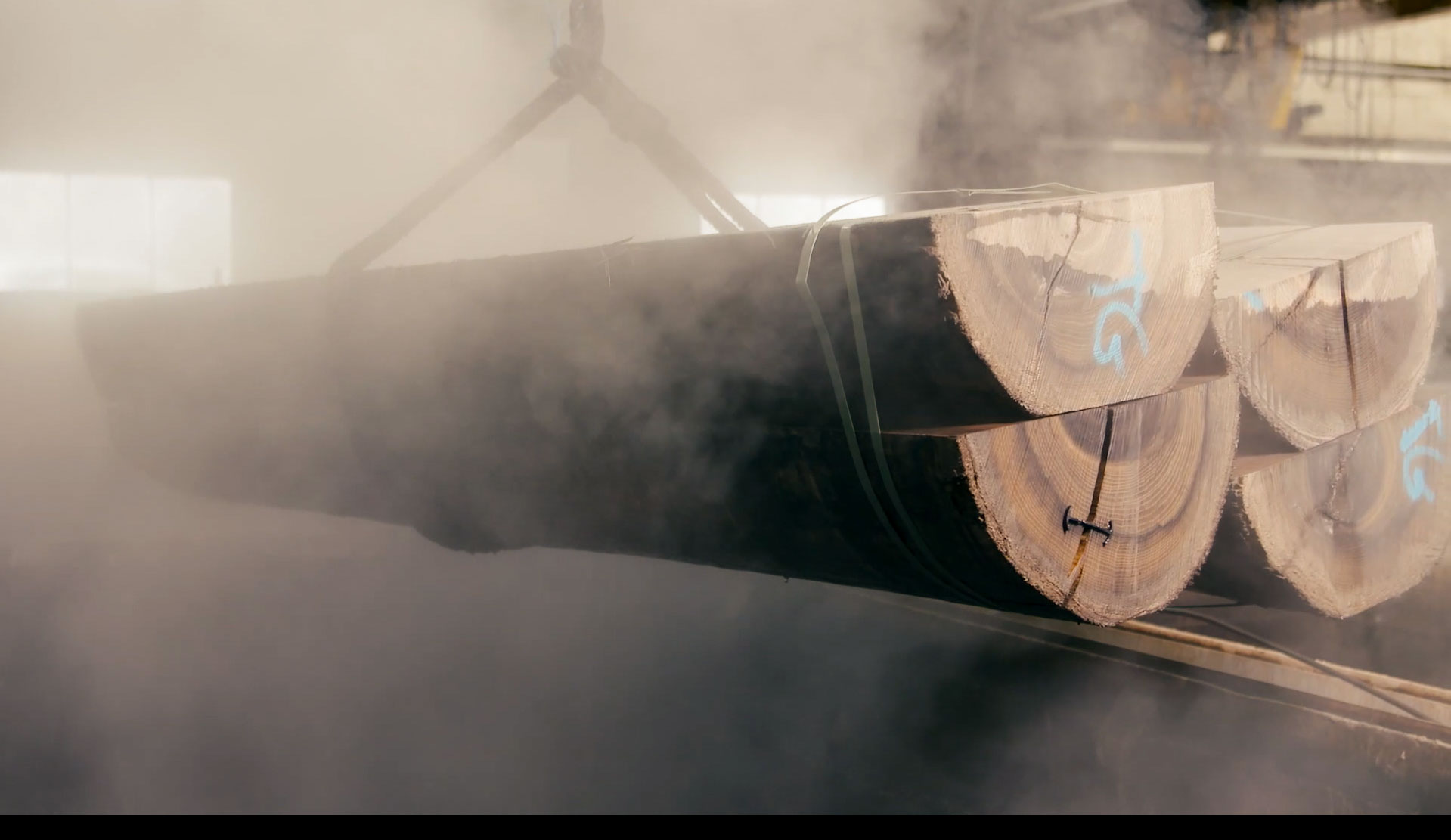
 Log Conditioning
Log ConditioningLogs are often soaked in hot water vats. This softens the wood, making it easier to remove the bark and cut into strands without creating excessive splinters or powdery waste.
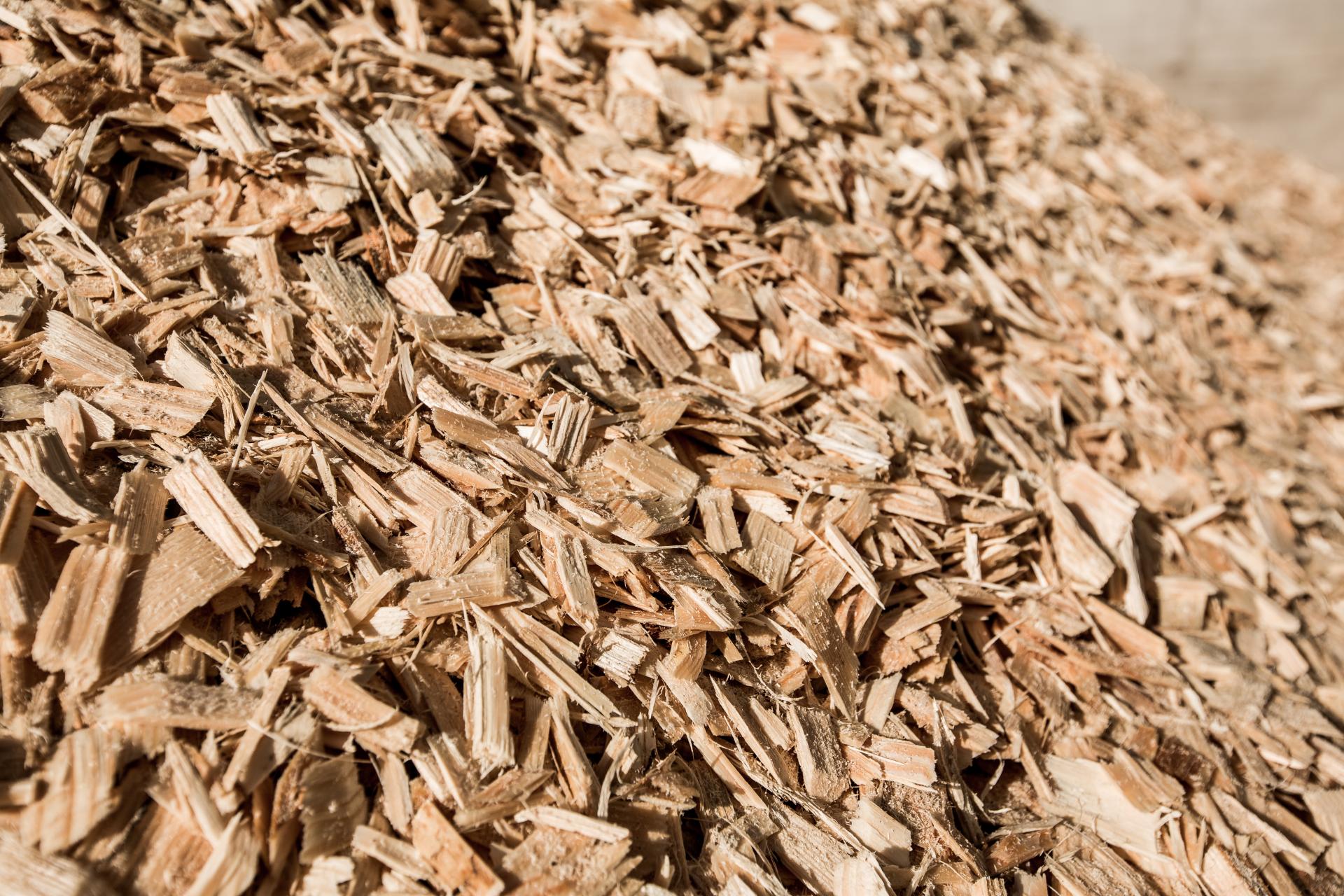



 Waferizing
WaferizingDebarked logs are fed into machines with sharp knives that rotate at high speeds. These knives slice the wood into long, flat flakes called strands, oriented in the direction of the grain.


 Drying
DryingThe wood strands are conveyed through large dryers to remove excess moisture. Precise moisture control (typically below 3%) is crucial for proper adhesive bonding and board stability.
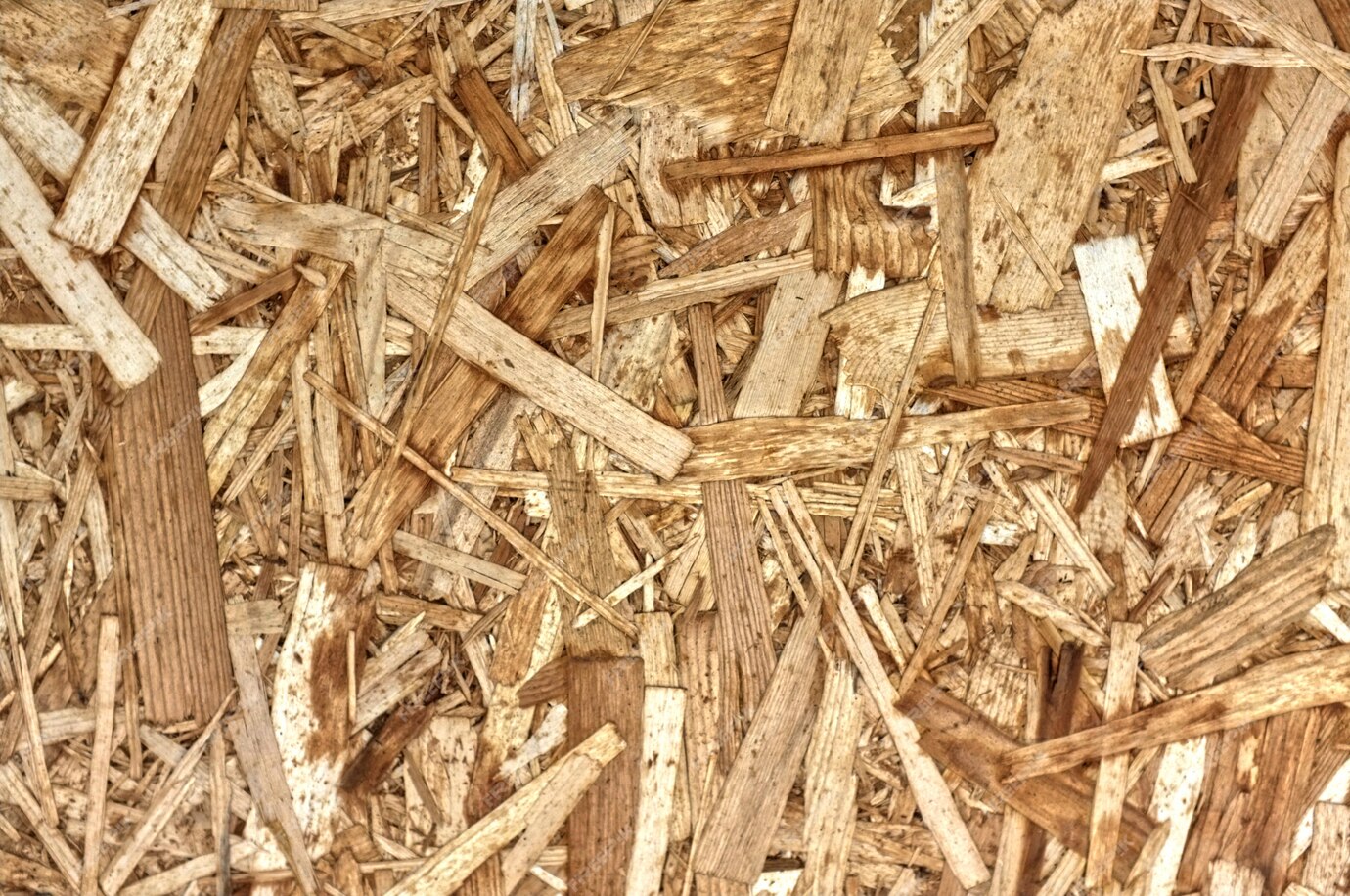


 Blending and Resin Application
Blending and Resin ApplicationDried strands are separated into different sizes. Larger strands are typically used for the surface layers, while smaller ones go into the core. These strands are then blended with a resin adhesive (often with additives for strength and moisture resistance) in large mixing drums.

 Forming and Mat Making
Forming and Mat MakingThe blended mixture of strands and resin is spread out in a precise way to form a “mat” with alternating layers. The surface layers have the strands oriented longitudinally (lengthwise) for added strength, while the core layer strands are oriented perpendicularly for stability.
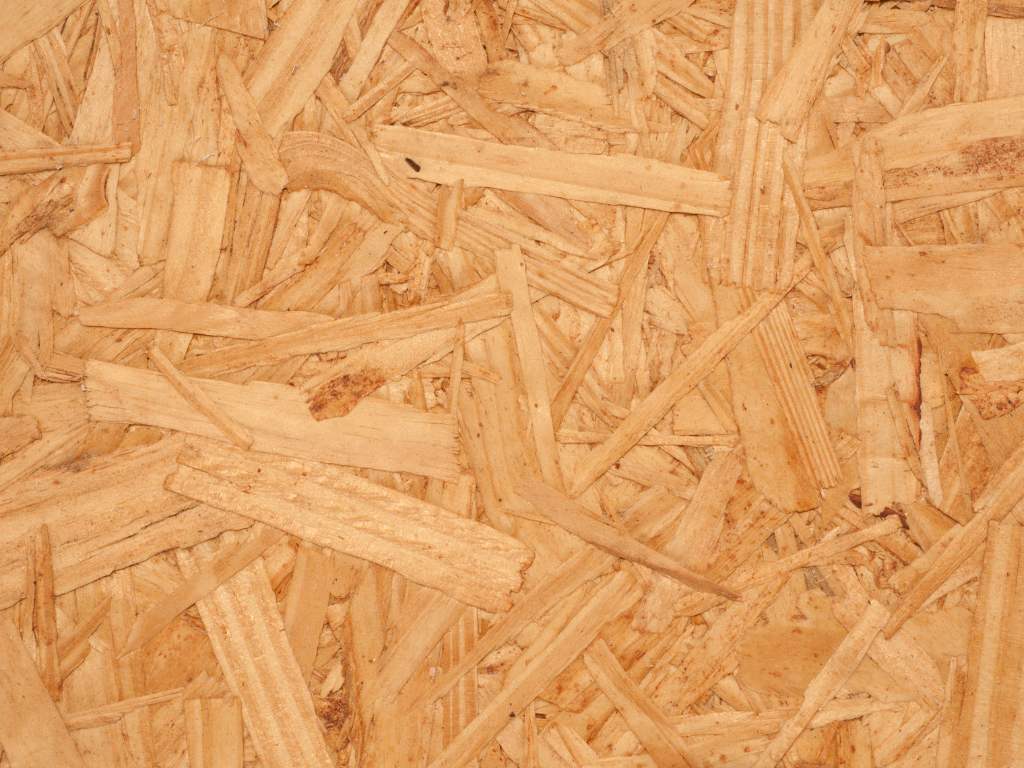


 Pressing
PressingThe formed mat is loaded into a continuous hot press. The intense heat and pressure activate the resin, causing it to cure and permanently bind the wood strands together into a solid panel.


 Finishing
FinishingAfter exiting the press, the panels are cooled, trimmed to their final size, sanded if needed, and inspected for quality. Depending on the application, some manufacturers may also apply edge sealants for improved moisture resistance.
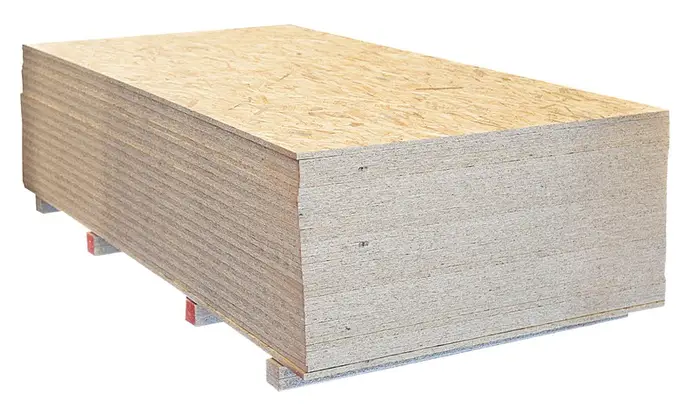



 Grading and Packaging
Grading and PackagingFinished OSB boards are graded based on factors like strength, moisture resistance, and surface quality. They are then stacked, strapped, labeled, and readied for shipment to distributors and building material retailers.

OSB boards boast a wide range of applications in construction projects, from structural elements to interior uses. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most common:
Structural Applications:
Interior Uses and Applications:
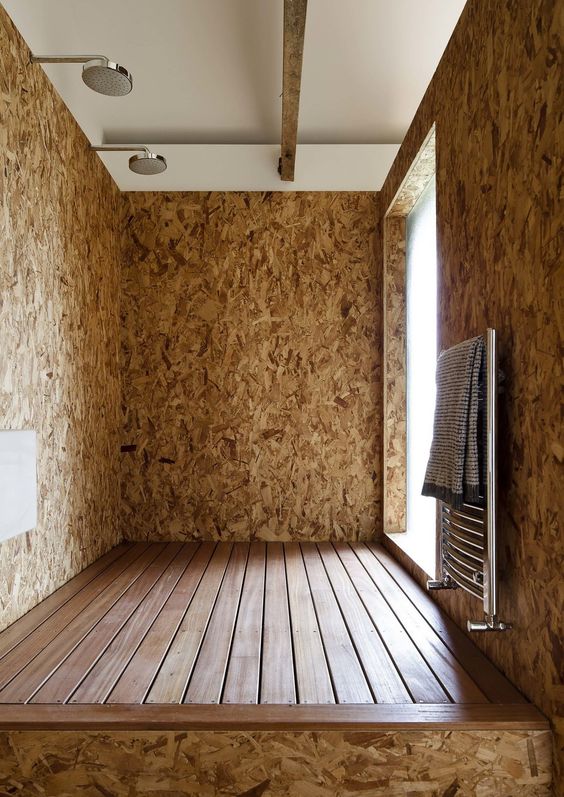
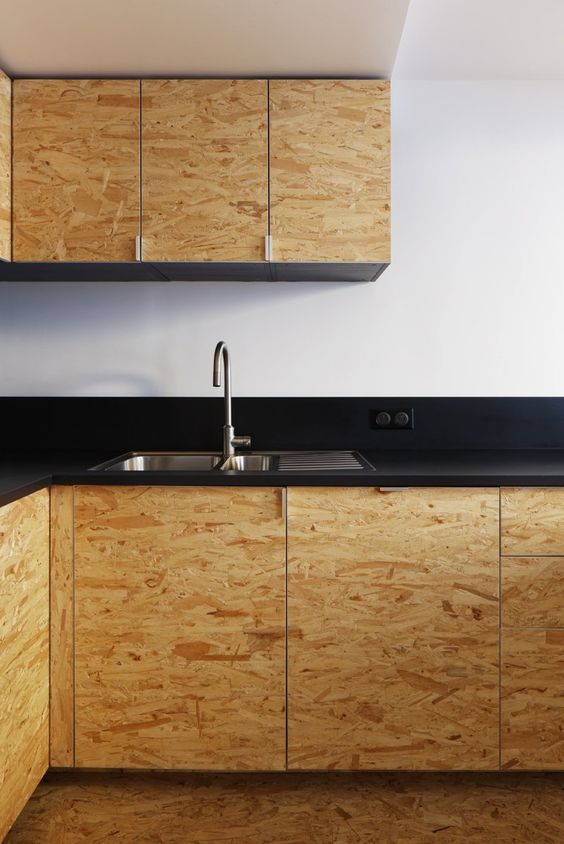





Benefits of OSB Boards:



